Composite Parts
| Registry Code | Part Name | Function | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BBa_25R1OZ0W⤴ | PCMV - IgK - Nluc - FS - TMD - mCherry - BGHPA | Expresses a constitutively secreted NanoLuc luciferase fused to a transmembrane anchor and mCherry reporter, serving as an unregulated control for secretion efficiency. | 1167 |
| BBa_250EVBWI⤴ | PCMV-IgK-Nluc - FS– TMD-mCherry - LifeAct - BGHPA | Encodes NanoLuc tethered to the cytoskeleton via LifeAct for visualization and analysis of vesicle retention independent of external signals. | 1880 |
| BBa_25RPYT7R⤴ | PCMV-LifeAct-CarH - BGHPA | Produces a cytoskeleton-anchored, green-light–sensitive CarH fusion protein used to control protein interactions via light-induced dissociation. | 1110 |
| BBa_252RTW6P⤴ | PCMV-IgK-Nluc-FS-TMD-_2GSlinker-CarH - BGHPA | Encodes a secreted NanoLuc fusion linked to the CarH photosensor, allowing light-dependent vesicle release and secretion. | 1746 |
| BBa_25NHFT5Q⤴ | PCMV-IgK-Nluc-FS-TMD-BphP1 - BGHPA | Expresses a secreted NanoLuc fused to the near-infrared light sensor BphP1 for red/NIR-controlled protein release. | 3327 |
| BBa_25LJBOAU⤴ | PCMV-LifeAct-BphP1 - BGHPA | Encodes a LifeAct-anchored BphP1 phytochrome fusion for cytoskeletal localization and optogenetic control under far-red illumination. | 2704 |
| BBa_25TK8QFS⤴ | PCMV-PpsR2 - BGHPA | Expresses the far-red light-responsive transcriptional regulator PpsR2 to evaluate its interaction dynamics with BphP1. | 1786 |
| BBa_25NYLBFF⤴ | PCMV-Binder-mCherry-LifeAct-BGHPA | Encodes a red fluorescent Binder fusion anchored to the cytoskeleton, enabling small-molecule-controlled association and dissociation with NS3a. | 1264 |
| BBa_25WEPAKX⤴ | PCMV-IgK-(Nluc - FS)_3-TMD-NS3a_2 - BGHPA | Encodes a secretory NanoLuc fusion bearing tandem NS3a domains for drug-inducible interaction with Binder and rapid, Grazoprevir-triggered secretion. | 3411 |
| BBa_2506II6Z⤴ | PCMV-IgK-Fluc-TMD-NS3a-BGHPA | Produces a membrane-anchored firefly luciferase fusion containing the NS3a domain for small-molecule–responsive secretion assays. | 2751 |
| BBa_2596NLG0⤴ | PCMV-Binder-TetR-NLS-VP64-BGHPA | Encodes a modular transcriptional activator combining Binder-TetR interaction, nuclear localization, and VP64 activation domain for drug-responsive gene expression. | 1339 |
| BBa_25EPQC3P⤴ | TCE-IgK-Nluc - BGHPA | Drives expression of secreted NanoLuc under a Tet-controlled element (TCE) promoter to evaluate transcriptional activation efficiency in small-molecule systems. | 1165 |
| BBa_25PW9O16⤴ | PCMV-GNCR-GSlinker-NLS-VP64- BGHPA | Produces a GNCR-based nuclear transcriptional activator responsive to NS3a interaction, enabling signal-controlled reporter gene induction. | 1327 |
| BBa_25NDCL0K⤴ | PCMV -TetR-NLS-NS3a-BGHPA | Encodes a TetR-NS3a fusion localized to the nucleus, forming part of the drug-controlled transcriptional activation system. | 1735 |
| BBa_25QZZZ22⤴ | PCMV-IgK-(Nluc - FS)_2-TMD-NS3a_2 - BGHPA | Expresses a dual-copy NanoLuc fusion with two NS3a domains for optimized signal responsiveness and enhanced secretion control. | 2880 |
| BBa_25B4NQ85⤴ | PCMV-IgK-Nluc - FS-TMD-NS3a_2 - BGHPA | Encodes a single-NanoLuc fusion containing two NS3a units to balance basal retention and drug-induced secretion sensitivity. | 2349 |
| BBa_25UUGKON⤴ | PCMV-IgK-Nluc - FS-TMD-NS3a - BGHPA | Expresses a secretory NanoLuc coupled with a single NS3a domain, enabling basic evaluation of small-molecule-triggered release kinetics. | 1719 |
| BBa_25YVM5DM⤴ | PCMV-IgK-Nluc - FS-TMD-NS3a_3 - BGHPA | Encodes a NanoLuc fusion bearing three NS3a domains to investigate multivalent effects on vesicle retention and response amplitude. | 2979 |
| BBa_25M95JXL⤴ | PCMV-EGFP-TMD-LifeAct-BGHPA | Produces a green fluorescent fusion protein anchored to the cytoskeleton, enabling visualization of vesicle immobilization. | 1302 |
| BBa_2578SBJ3⤴ | PCMV-LifeAct-mCherry-BGHPA | Expresses a red fluorescent LifeAct fusion for real-time visualization of F-actin organization and anchoring behavior. | 559 |
| BBa_25IZYJLX⤴ | PCMV - EGFP - TMD-BGHPA | Encodes a membrane-localized green fluorescent protein serving as a reference for plasma-membrane targeting efficiency. | 1230 |
| BBa_25W216DF⤴ | PCMV-IgK-Nluc- BGHPA | Expresses a secreted NanoLuc luciferase as a baseline control for secretion assays. | 1033 |
| BBa_25WLRLM7⤴ | PCMV-IgK-Nluc-TMD-mMaple3-LifeAct - BGHPA | Produces a cytoskeleton-anchored, blue-violet–light–regulated NanoLuc fusion for photolytically controlled protein secretion. | 1950 |
Favourite Composite Part
Part Name: PCMV-IgK-(Nluc-FS)3-TMD-(NS3a)2-BGHPA
Part ID: BBa_25WEPAKX
Overview
Inspired by the regulated secretion mechanisms of neurons and pancreatic β-cells, we designed a rapid-response, drug-inducible protein secretion switch based on the chemically induced dissociation of NS3a and Binder1.
Our favorite composite part, PCMV-IgK-(Nluc-FS)3-TMD-(NS3a)2-BGHPA (BBa_25WEPAKX), forms the core secretion module of our system. It functions together with the anchoring module PCMV-Binder-mCherry-LifeAct-BGHPA (BBa_25NYLBFF) to build chemSPARK, a modular secretion control platform (See our Design and Results page).
Under normal conditions, the NS3a-Binder interaction anchors secretory vesicles to the actin cytoskeleton, preventing release. When cells are exposed to Grazoprevir, an FDA-approved NS3a inhibitor, the drug disrupts the NS3a-Binder complex, triggering immediate vesicle release and rapid protein secretion (Figure 1).
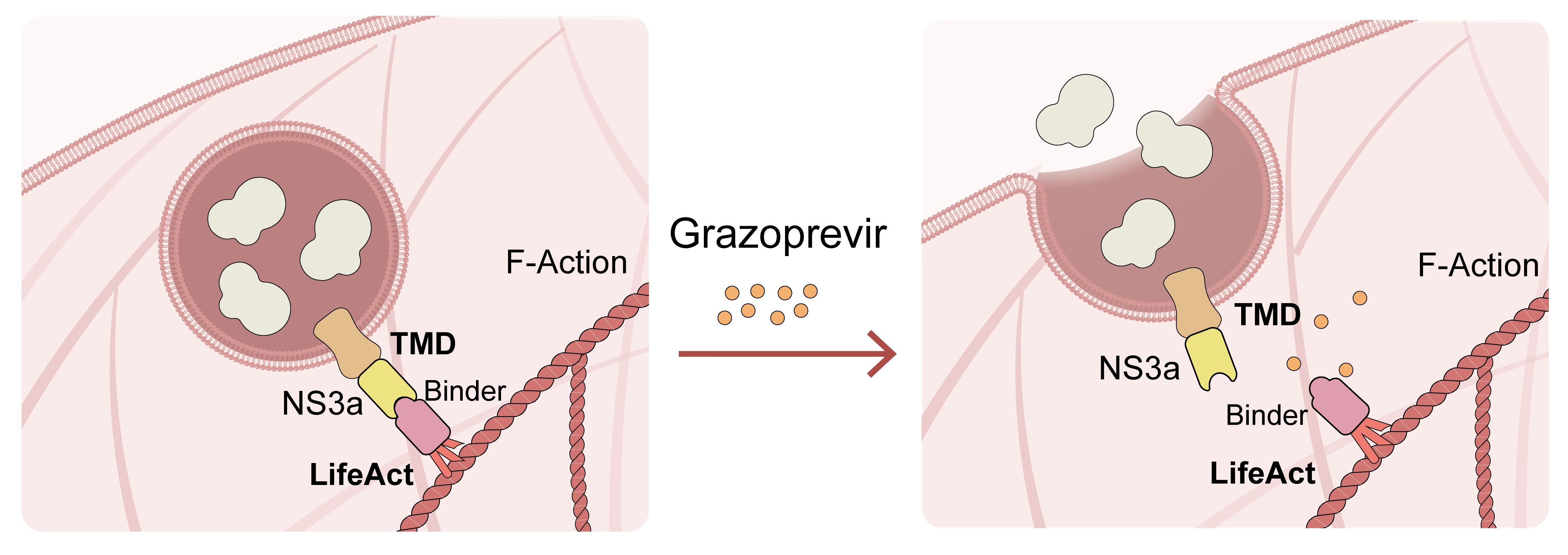
Figure 1.Schematic illustration of the secretion ON system mediated by Grazoprevir-induced NS3a-Binder dissociation.(TMD, transmembrane domain).
Component Description
| Module | Registry ID | Function |
|---|---|---|
| PCMV | BBa_K5073031⤴ | A strong constitutive mammalian promoter derived from cytomegalovirus, driving high-level expression. |
| IgK Signal Peptide | BBa_K3117006⤴ | Directs the nascent polypeptide into the secretory pathway via the ER-Golgi route. |
| Nluc (NanoLuc Luciferase) | BBa_K2728003⤴ | A small, bright luminescent reporter used to quantify secretion activity. |
| Furin Cleavage Site (FS) | BBa_25K5NJ9H⤴ | Enables proteolytic separation of the reporter protein from the TMD during vesicle trafficking. |
| TMD (Transmembrane Domain) | BBa_25J460FA⤴ | Anchors the fusion protein to vesicle or plasma membranes, positioning NS3a on the cytosolic side. |
| NS3a (HCV Protease Domain) | BBa_25HYFBUH⤴ | Binds to Binder under physiological conditions but dissociates upon Grazoprevir treatment. |
| BGHPA | BBa_K1150012⤴ | A bovine growth hormone polyadenylation signal for efficient mRNA transcription termination. |
Together, these elements form a functional composite that enables drug-responsive secretion control through regulated vesicle anchoring and release.
Experimental Validation
Methods
Cell Culture and Transfection
HEK293T cells (ATCC CRL-3216) were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin-streptomycin at 37 °C and 5% CO₂. Cells were seeded at 5 × 104 per well in 24-well plates and transfected 12 h later using a PEI-based protocol (PEI:DNA = 5:1, w/w). HEK293T cells were co-transfected with pNC25092 (PCMV-IgK-(Nluc)3-TMD-(NS3a)2) and either pNC25086 (PCMV-LifeAct-mCherry; control) or pNC25091 (PCMV-Binder-LifeAct).The transfection mix was replaced with fresh medium 6 h post-transfection. Transfection was performed at 16 h after seeding 5 × 104 mammalian cells into each well of a 24-well plate. The cell culture medium was replaced with fresh medium (not containing transfection reagents) at 6 h after transfection. HEK-293T cells were transfected using a PEI-based protocol at a PEI:DNA ratio of 5:1 (w/w) and in a transfection volume of 50 μL native serum-free DMEM per well.
Reporter Quantification
Secreted NanoLuc levels were measured from cell culture supernatants using the Nano-Glo Luciferase Assay System (Promega, N1120). All measurements were performed in biological quadruplicates (n = 4). Statistical analyses used two-tailed unpaired t-tests (P<0.05 considered significant).
Result
To test the secretion switch, HEK293T cells were co-transfected with plasmids carrying PCMV-IgK-(Nluc-FS)3-TMD-(NS3a)2-BGHPA (BBa_25WEPAKX) and plasmids carrying PCMV-Binder-mCherry-LifeAct-BGHPA (BBa_25NYLBFF) at a 1:3 DNA ratio (100 ng : 300 ng per well).
After 48 h, cells were treated with 10 µM Grazoprevir (experimental group) or DMSO (control). Supernatants were collected 2 h post-treatment for NanoLuc quantification. Cells treated with Grazoprevir showed a significant increase in NanoLuc secretion, confirming that NS3a-Binder dissociation releases pre-anchored vesicles and activates rapid protein secretion (Figure 2).
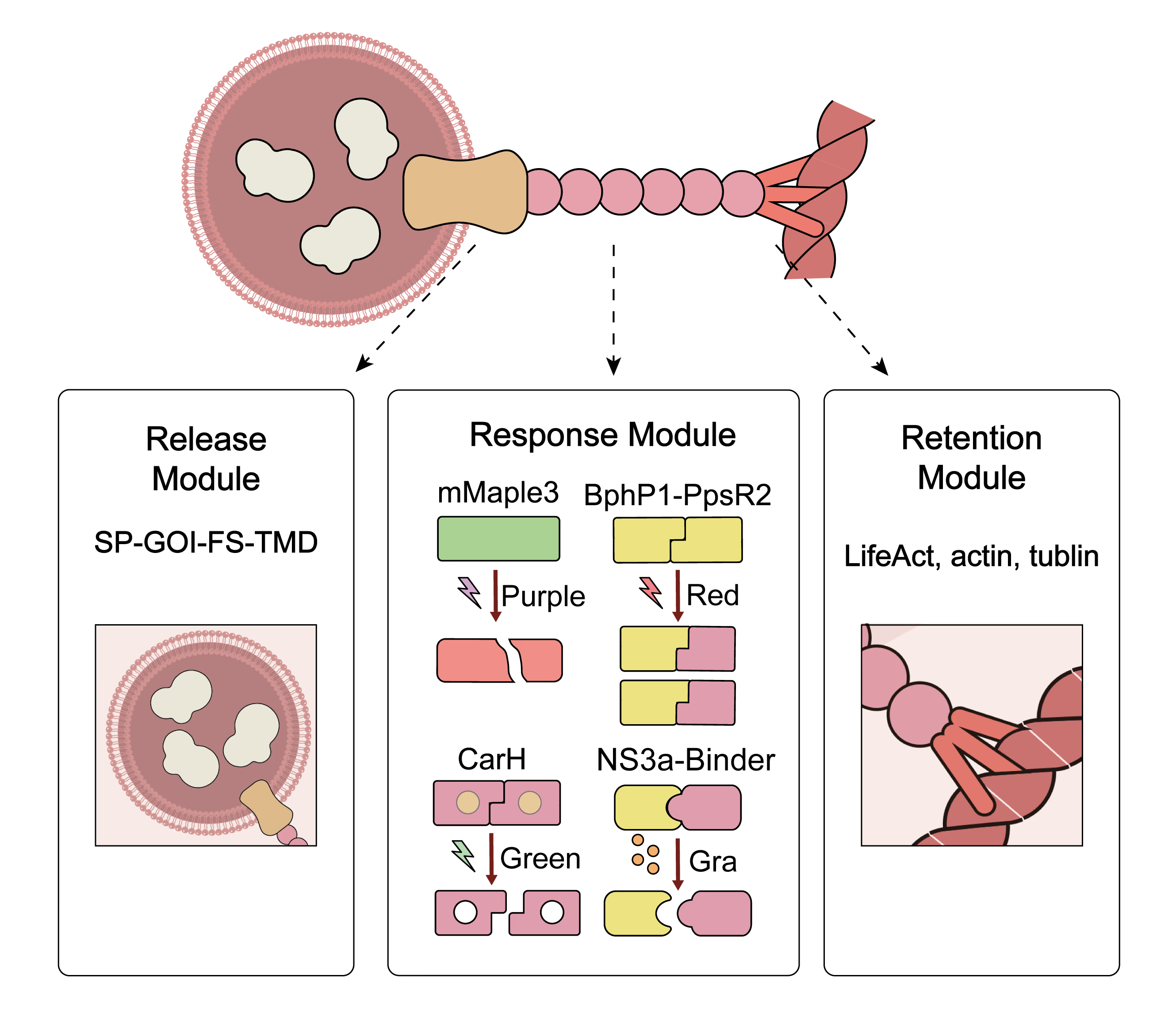
Figure 2.NanoLuc levels in culture supernatants 2 h after Grazoprevir (10 µM) or DMSO treatment. Data shown as mean ± SD (n = 4); ***P<0.001.
Characterization
Dynamic Response
To assess activation kinetics, HEK293T cells were co-transfected with plasmids carrying PCMV-IgK-(Nluc-FS)3-TMD-(NS3a)2-BGHPA (BBa_25WEPAKX) and plasmids carrying PCMV-Binder-mCherry-LifeAct-BGHPA (BBa_25NYLBFF) at a 1:3 DNA ratio (100 ng : 300 ng per well).. Cells were then treated with 10 µM Grazoprevir or DMSO and supernatants were collected at a series of different time points within 24 hours post-treatment.
NanoLuc secretion rose rapidly within the first hour and peaked around 3 h, reaching an approximate 40-fold induction relative to untreated controls (Figure 3).
These results demonstrate that the secretion switch responds dynamically to drug input, achieving full activation within hours.
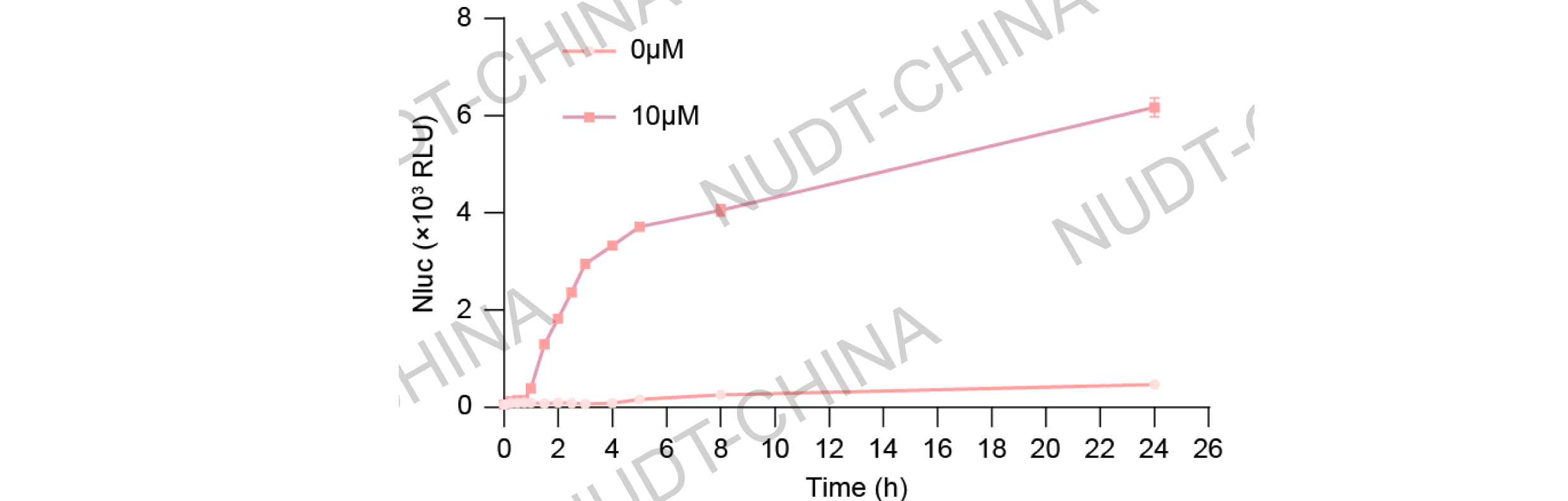
Figure 3.Time-course of NanoLuc secretion following Grazoprevir stimulation (10 µM). Mean ± SD, n = 3.
Dose-Dependent Response
To characterize dose sensitivity, cells were treated with a gradient of Grazoprevir concentrations (0-10 µM) 48 h after transfection. Supernatants were collected 2 h post-stimulation for NanoLuc measurement. The system exhibited graded, dose-dependent activation, with secretion increasing steadily from 100 nM and peaking at 10 µM Grazoprevir, where a maximum 40-fold induction was observed (Figure 4).
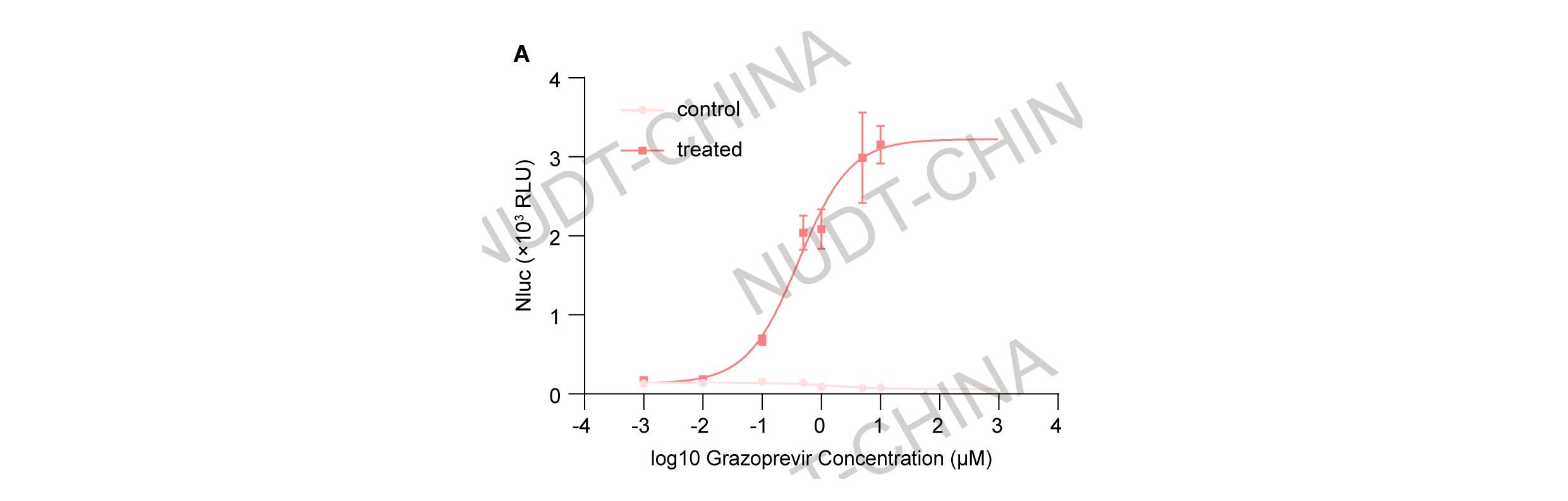
Figure 4.Dose-dependent secretion response to Grazoprevir treatment (0-10 µM). Data presents mean ±SD, n = 3 independent experiments, fitted to a symmetric sigmoid curve.
Future Applications
While NanoLuc serves as the reporter in our prototype, it can be readily replaced with user-defined therapeutic or functional proteins, allowing teams to adapt the system to diverse applications. For example, the secretion module could be reprogrammed to release insulin or pramlintide for diabetes therapy2, atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) for cardiac function regulation3, or phytohormones for controlled agricultural biomanufacturing4.
Conclusion
The composite part PCMV-IgK-(Nluc-FS)3-TMD-(NS3a)2-BGHPA serves as the core output module of our chemSPARK system. It enables rapid, tunable, and reversible control of protein secretion in mammalian cells through drug-induced protein dissociation.
This part demonstrates the feasibility of building post-translational gene switches that respond to clinically relevant small molecules, offering a powerful foundation for therapeutic protein delivery, synthetic cell communication, and dynamic regulation in mammalian synthetic biology.
 Description
Description
 Design
Design
 Notebook
Notebook
 Results
Results
 Basic Parts
Basic Parts
 Composite Parts
Composite Parts
 Parts Collection
Parts Collection
 Education
Education
 Art Gallery
Art Gallery
 Implementation
Implementation
 Attributions
Attributions
 Collaboration
Collaboration